
Outline of the Article
Introduction
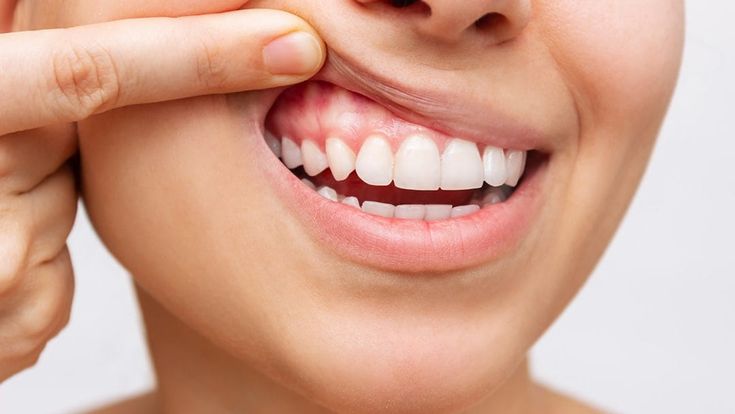
Gum diseases, also known as periodontal diseases, are common conditions affecting the gums and supporting structures of the teeth. They can range from mild gingivitis to more severe forms that can lead to tooth loss if left untreated.
Understanding Gum Diseases!!!
Types of Gum Diseases
There are several types of gum diseases, including:
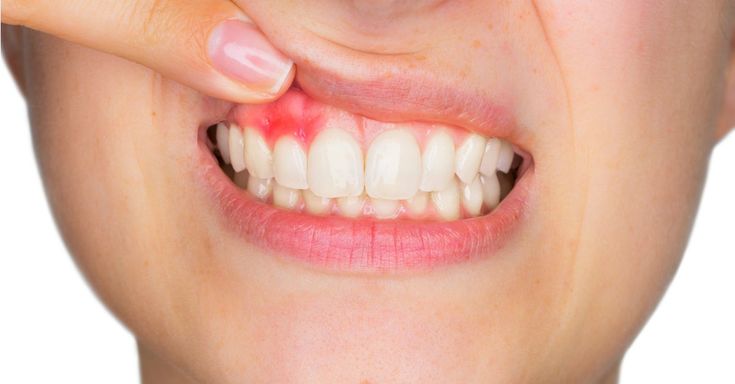
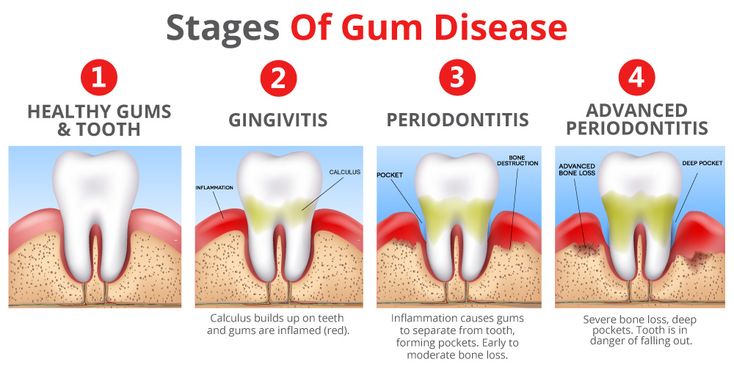
– Gingivitis: This is the early stage of gum disease, characterized by inflammation of the gums.
– Periodontitis: If gingivitis is left untreated, it can progress to periodontitis, where the infection spreads to the supporting structures of the teeth.
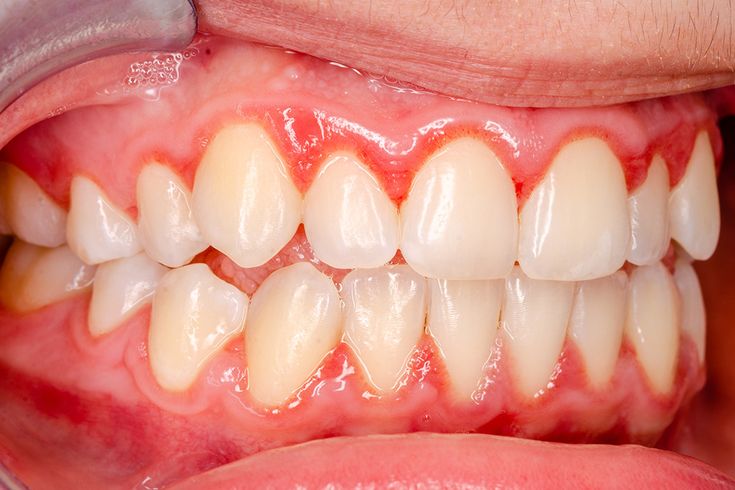
Causes of Gum Diseases
Gum diseases are primarily caused by poor oral hygiene that leads to the accumulation of plaque -a sticky film of bacteria on the teeth.
Other factors contributing to gum diseases include smoking, hormonal changes, certain medications, and genetic predisposition

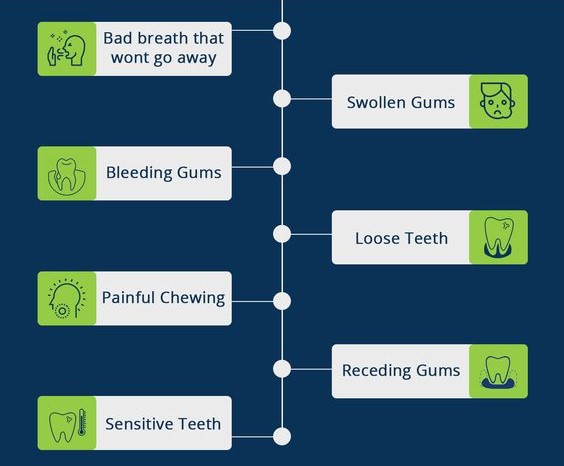
Symptoms of Gum Diseases
EARLY SIGNS ADAVNCED SYMPTOMS
Risk Factors
Certain factors increase the risk of developing gum diseases, such as smoking, diabetes, aging, stress, and poor nutrition.
Impact of Gum Diseases on Oral Health
Untreated gum diseases can have serious consequences, including tooth loss, bone loss in the jaw, and increased risk of systemic diseases like heart disease and diabetes.
Diagnosis of Gum Diseases
Dentists diagnose gum diseases through a combination of visual examination, probing of the gums, and X-rays to assess bone loss.
Treatment Options
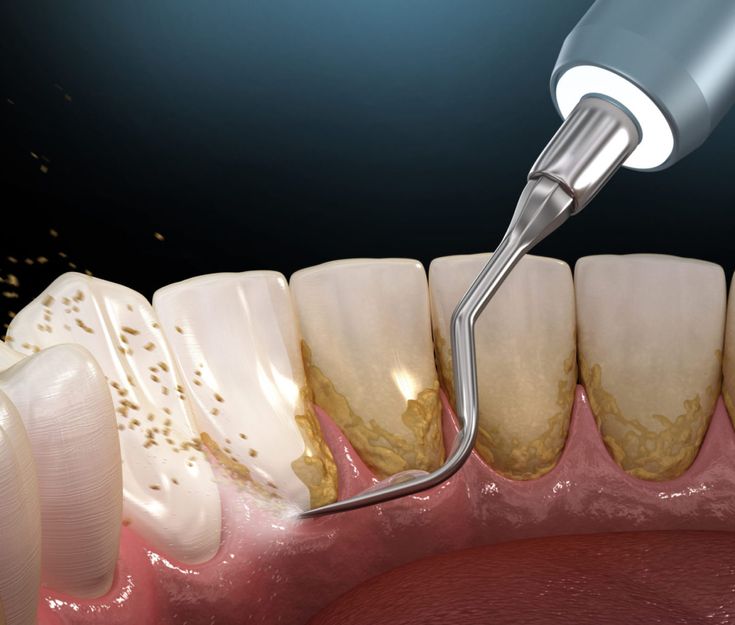
Non-Surgical Treatments
– Scaling and root planning (deep cleaning)
– Antibiotics to control bacterial infection
– Dental irrigation
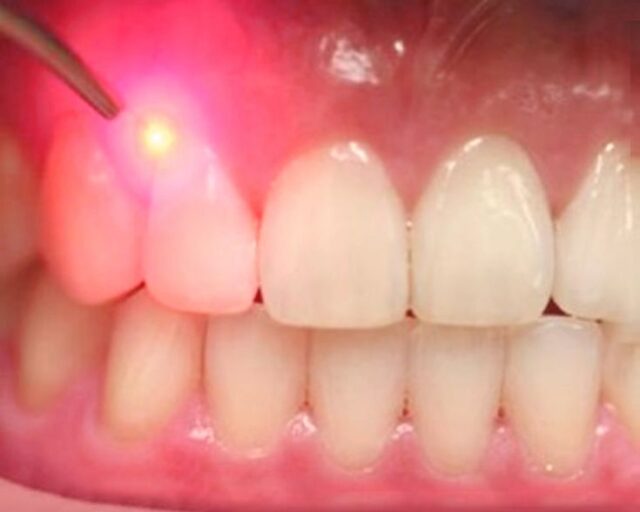
Surgical Treatments
– Flap surgery to remove tartar deposits
– Bone grafts or tissue regeneration
– Laser therapy to remove infected tissue
Preventive Measures
Home Remedies for Gum Health
Dietary Tips for Preventing Gum Diseases
A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins can promote gum health and overall oral hygiene.

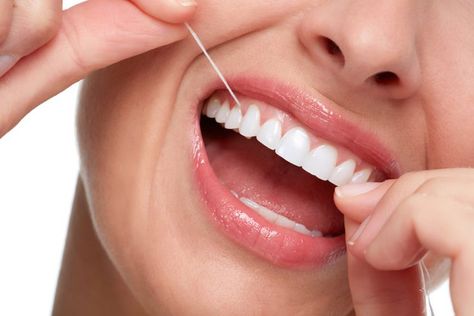


Importance of Oral Hygiene
Regular brushing and flossing help remove plaque and prevent the onset of gum diseases
Common Misconceptions about Gum Diseases

Myth: Gum disease only affects older adults.
Fact: Gum diseases can occur at any age, especially with poor oral hygiene.

When to See a Dentist
It’s crucial to consult a dentist if you notice any signs or symptoms of gum diseases, such as bleeding gums or persistent bad breath.
Conclusion
In conclusion, gum diseases can manifest with various symptoms and can have significant impacts on oral and overall health if left untreated. Early detection, proper diagnosis, and timely treatment are essential in managing gum diseases effectively.
FAQs
– Early stages of gum diseases like gingivitis can be reversed with proper oral care.
– Home remedies can complement professional treatments but may not replace them entirely.
– Yes, untreated gum diseases have been linked to increased risks of heart disease and diabetes.
– Regular dental check-ups every 6 months are recommended to monitor gum health.
– Yes, smoking weakens the immune system and increases the risk of gum diseases.





Outline of the Article
Introduction
Gum diseases, also known as periodontal diseases, are common conditions affecting the gums and supporting structures of the teeth. They can range from mild gingivitis to more severe forms that can lead to tooth loss if left untreated.

Understanding Gum Diseases!!!
Types of Gum Diseases
There are several types of gum diseases, including:
– Gingivitis: This is the early stage of gum disease, characterized by inflammation of the gums.
– Periodontitis: If gingivitis is left untreated, it can progress to periodontitis, where the infection spreads to the supporting structures of the teeth.

Causes of Gum Diseases
Gum diseases are primarily caused by poor oral hygiene that leads to the accumulation of plaque -a sticky film of bacteria on the teeth.
Other factors contributing to gum diseases include smoking, hormonal changes, certain medications, and genetic predisposition

Symptoms of Gum Diseases
EARLY SIGNS ADAVNCED SYMPTOMS

Risk Factors
Certain factors increase the risk of developing gum diseases, such as smoking, diabetes, aging, stress, and poor nutrition.
Impact of Gum Diseases on Oral Health
Untreated gum diseases can have serious consequences, including tooth loss, bone loss in the jaw, and increased risk of systemic diseases like heart disease and diabetes.

Diagnosis of Gum Diseases
Dentists diagnose gum diseases through a combination of visual examination, probing of the gums, and X-rays to assess bone loss.
Treatment Options
Non-Surgical Treatments
– Scaling and root planning (deep cleaning)
– Antibiotics to control bacterial infection
– Dental irrigation

Surgical Treatments
– Flap surgery to remove tartar deposits
– Bone grafts or tissue regeneration
– Laser therapy to remove infected tissue

Preventive Measures
Home Remedies for Gum Health
Dietary Tips for Preventing Gum Diseases
A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins can promote gum health and overall oral hygiene.




Importance of Oral Hygiene
Regular brushing and flossing help remove plaque and prevent the onset of gum diseases
Common Misconceptions about Gum Diseases

Myth: Gum disease only affects older adults.
Fact: Gum diseases can occur at any age, especially with poor oral hygiene.

When to See a Dentist
It’s crucial to consult a dentist if you notice any signs or symptoms of gum diseases, such as bleeding gums or persistent bad breath.
Conclusion
In conclusion, gum diseases can manifest with various symptoms and can have significant impacts on oral and overall health if left untreated. Early detection, proper diagnosis, and timely treatment are essential in managing gum diseases effectively.
FAQs
– Early stages of gum diseases like gingivitis can be reversed with proper oral care.
– Home remedies can complement professional treatments but may not replace them entirely.
– Yes, untreated gum diseases have been linked to increased risks of heart disease and diabetes.
– Regular dental check-ups every 6 months are recommended to monitor gum health.
– Yes, smoking weakens the immune system and increases the risk of gum diseases.