Outline
Introduction to Teeth Pain
Maintaining Good Oral Hygiene
Dietary Habits and Teeth Health
Avoiding Harmful Habits
Choosing the Right Dental Products
Protective Measures for Teeth
Dealing with Dental Emergencies
Mind-Body Connection
Home Remedies for Teeth Pain
Understanding Dental Anatomy
Preventive Measures for Different Age Groups
The Role of Genetics
Educational Campaigns and Resources
Common Myths and Misconceptions
Conclusion
Teeth pain can be excruciating and often disrupts daily life activities.
However, with proper care and preventive measures, you can significantly reduce the risk of experiencing dental discomfort.
This comprehensive guide covers effective strategies to prevent teeth pain and maintain optimal oral health.
Introduction to teeth pain
Teeth pain can result from various factors, including dental decay, gum disease, tooth sensitivity, or dental injuries.
Understanding the causes of teeth pain is crucial in adopting preventive measures to avoid discomfort and potential complications.
Prevention is always better than cure when it comes to dental health.
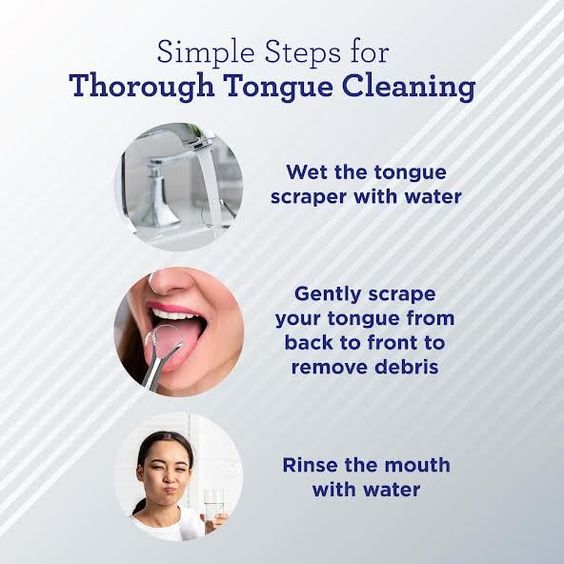
Maintaining Good Oral Hygiene
Proper oral hygiene practices are fundamental in preventing teeth pain.
Brushing your teeth at least twice a day using fluoride toothpaste, along with regular flossing, helps remove food particles and plaque that can lead to tooth decay and gum disease.
Additionally, scheduling routine dental check-ups enables early detection of potential issues before they escalate into severe problems.
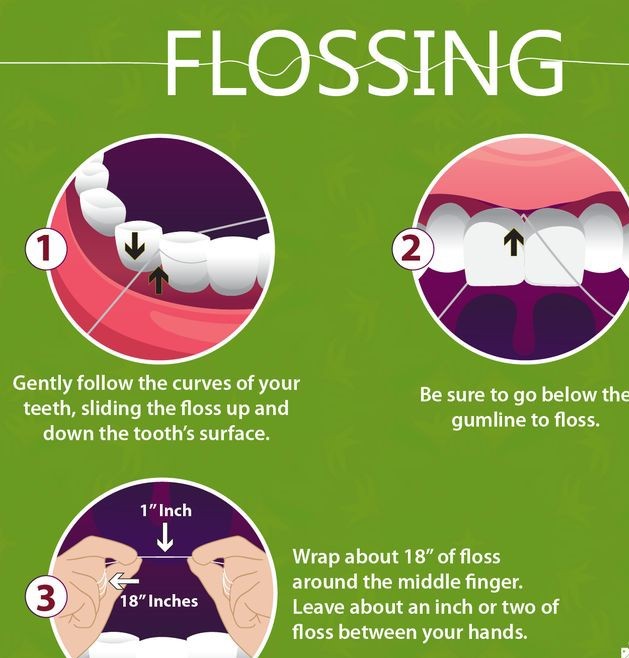
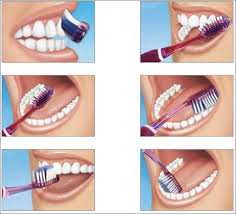
Dietary Habits and Teeth Health
Diet plays a significant role in dental health.
Avoiding excessive consumption of sugary and acidic foods can help prevent tooth decay and erosion.
Instead, focus on incorporating tooth-friendly foods like dairy products, crunchy fruits, and vegetables that promote saliva production and neutralize acids in the mouth.


Avoiding Harmful Habits
Certain habits, such as smoking and excessive teeth grinding (bruxism), can contribute to teeth pain and other dental problems.
Quitting smoking not only improves overall health but also reduces the risk of gum disease and oral cancers.
Using a mouthguard can help protect teeth from damage caused by bruxism.


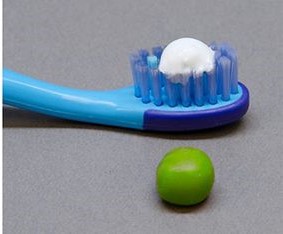
Choosing the Right Dental Products
Selecting the right dental products is essential for maintaining oral health.
Opt for toothpaste and mouthwash containing fluoride, a mineral that strengthens tooth enamel and reduces the risk of cavities.
Your dentist can recommend specific products tailored to your dental needs.

Protective Measures for Teeth
Engaging in activities that pose a risk to dental health, such as contact sports, warrants the use of mouthguards to prevent dental injuries.
Additionally, preventive treatments like dental sealants and fluoride applications can provide added protection against cavities.
Dealing with Dental Emergencies
In the event of sudden teeth pain or injury, it’s crucial to remain calm and seek professional dental care promptly.
Avoid self-medication and home remedies that may exacerbate the issue.
Dental emergencies require immediate attention to prevent further complications.
Mind-Body Connection
Stress and anxiety can manifest physically, including impacting dental health.
Practicing stress management techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises can alleviate tension and promote overall well-being, including dental health.

Home Remedies for Teeth Pain
While not substitutes for professional dental care, certain home remedies like rinsing with warm salt water or applying clove oil can provide temporary relief from teeth pain.
However, these remedies should complement rather than replace professional treatment.

Understanding Dental Anatomy
Knowing the structure of teeth and their functions can enhance awareness of dental health.
Each part of a tooth serves a specific purpose, and understanding these can aid in preventive care and recognizing potential dental issues.
Preventive Measures for Different Age Groups
Dental care requirements vary with age.
Children require supervision and assistance with brushing, and seniors may face unique challenges like dry mouth and gum recession.
Tailor dental care practices to address specific age-related needs.

The Role of Genetics
Genetic factors can influence dental health, making some individuals more susceptible to certain conditions like gum disease or enamel defects.
Understanding genetic predispositions can empower individuals to take proactive measures to mitigate risks.
Educational Campaigns and Resources
Spreading awareness about teeth pain prevention through educational campaigns and resources is essential.
Accessible information encourages proactive dental care and empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their oral health.
Common Myths and Misconceptions
Dispelling common myths and misconceptions about dental health is crucial in promoting accurate information.
Debunking myths like “milk teeth don’t need to be cared for” or “brushing harder cleans better” helps foster better dental practices.
Conclusion
Preventing teeth pain requires a proactive approach that encompasses proper oral hygiene, healthy dietary habits, avoidance of harmful behaviors, and regular dental visits.
By implementing these strategies, you can maintain optimal dental health and minimize the risk of teeth pain and related complications.
FAQs
How often should I visit the dentist to prevent teeth pain?
It’s recommended to visit the dentist at least twice a year for routine check-ups and cleanings.
Can stress cause teeth pain?
Yes, stress can contribute to teeth grinding (bruxism) and jaw tension, leading to teeth pain.
What foods should I avoid to prevent teeth pain?
Limit consumption of sugary snacks and acidic beverages to protect teeth from decay and erosion.
Are home remedies effective for treating teeth pain?
Home remedies can offer temporary relief, but professional dental care is essential for addressing underlying issues.
Is genetics a significant factor in dental health?
Genetics can influence susceptibility to certain dental conditions, but maintaining good oral hygiene can mitigate risks.